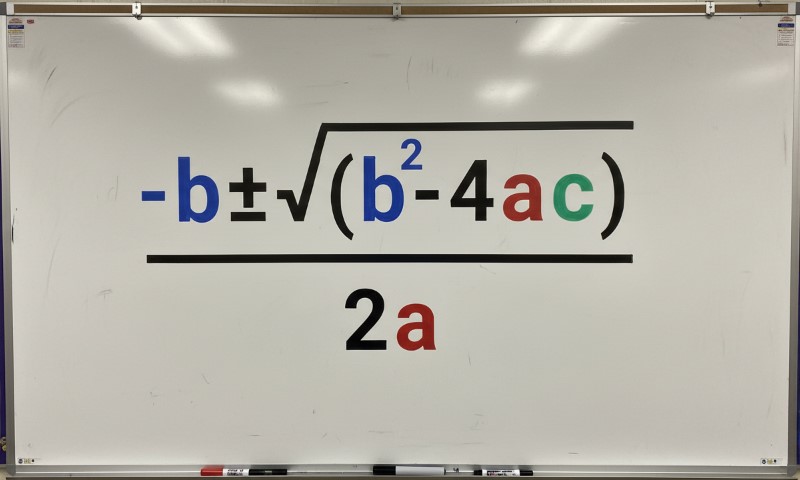
Share Post:
Quadratic equations show up any time a situation curves instead of moving in a straight line. A ball thrown into the air. Braking distance as speed increases. Profit that rises, peaks, then drops. Even architectural arches and simplified satellite paths land in quadratic territory.
When a relationship can be written as a second-degree polynomial, the quadratic formula gives a reliable way to find the solutions.
Many methods exist for solving quadratics. Factoring works when numbers behave nicely. The square root property helps once an equation isolates x². Completing the square has value when reshaping an equation or explaining where formulas come from.
The quadratic formula stands out because it works every time, even when the coefficients are awkward or refuse to factor cleanly.
Here is a practical, step-by-step guide written for real use, not memorization alone.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat a Quadratic Equation Looks Like
A quadratic equation in one variable usually appears in standard form:
ax² + bx + c = 0 , where a ≠ 0
Each piece has a job:
- a controls how wide or narrow the curve is and whether it opens up or down
- b shifts the curve sideways
- c sets the vertical starting point
Any method for solving quadratics begins by getting the equation into this form.
The Quadratic Formula (WordPress-Friendly Formatting)
When an equation sits in standard form, the quadratic formula gives the solutions directly:
x = ( -b ± √(b² – 4ac) ) / (2a)
Every symbol matters.
What Each Part Means
- a, b, c come straight from ax² + bx + c = 0
- ± means “plus or minus,” signaling two possible solutions
- √(b² – 4ac) contains the discriminant
- 2a forms the full denominator and must divide everything above it
Skipping or misplacing any of these pieces creates errors fast.
Step 0: Decide If the Formula Is the Right Tool

Before reaching for the formula, take five seconds to scan the equation.
- Factoring is fastest when numbers cooperate
- Square root property works once x² stands alone
- Completing the square helps when rewriting into vertex form
- Quadratic formula handles all quadratics in standard form, without exceptions
When coefficients include fractions, decimals, or large numbers, the quadratic formula usually saves time.
Step-by-Step – Solving With the Quadratic Formula
When numbers stop cooperating, and factoring turns messy, a clear step-by-step approach with the quadratic formula keeps the work organized and the answers reliable.
Step 1: Rewrite in Standard Form
Move every term to one side so the other side equals zero.
Example:
3x² = 5x − 2
becomes
3x² − 5x + 2 = 0
Nothing else works until this step is done correctly.
Step 2: Identify a, b, and c Carefully
From
3x² − 5x + 2 = 0
- a = 3
- b = −5
- c = 2
Write them down explicitly. Most mistakes start here, especially with the sign of b.
Step 3: Compute the Discriminant
The discriminant lives under the square root:
Δ = b² − 4ac
For example:
- b² = (−5)² = 25
- 4ac = 4·3·2 = 24
Δ = 25 − 24 = 1
Slow arithmetic here prevents bigger problems later.
Step 4: Substitute Into the Formula
x = ( −b ± √Δ ) / (2a)
Plug in carefully:
- −b = 5
- √Δ = 1
- 2a = 6
So:
x = (5 ± 1) / 6
Step 5: Split and Simplify
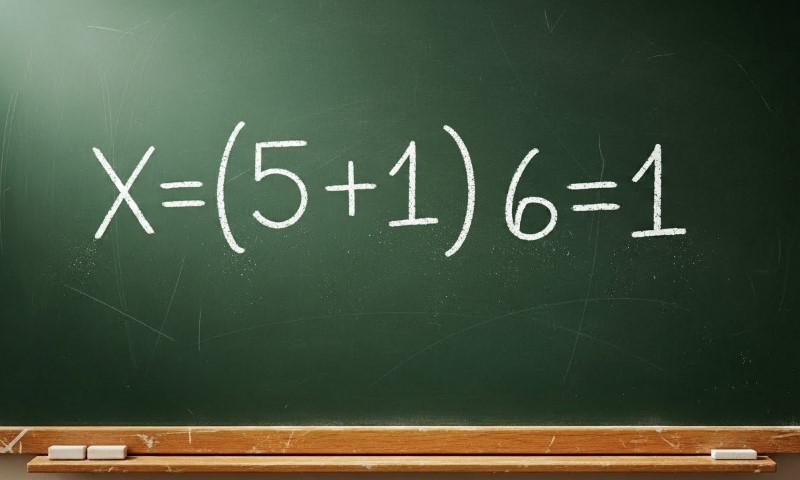
Two values come from ±.
- x = (5 + 1)/6 = 1
- x = (5 − 1)/6 = 2/3
Solutions: x = 1 and x = 2/3
Step 6: Check the Solutions
Substitute each value back into the original equation. A quick check catches sign slips or arithmetic errors. Regular checking is standard practice in solid equation-solving habits.
The Discriminant – Predicting Solutions Before Solving
The discriminant does more than sit under a radical. It predicts how many solutions exist and what type they are.
What the Discriminant Tells You
| Discriminant Value | Meaning | Graph Behavior |
| Δ > 0 | Two real solutions | Curve crosses the x-axis twice |
| Δ = 0 | One repeated solution | Curve touches the x-axis once |
| Δ < 0 | Two complex solutions | Curve never meets the x-axis |
These interpretations connect algebra directly to graphs and solution types
Worked Examples for Each Case
Real understanding settles in once the numbers start moving, so the examples below walk through each discriminant case step by step and show how the quadratic formula behaves in practice.
Example 1: Two Real Solutions (Δ > 0)
Solve:
x² − 5x + 6 = 0
- a = 1, b = −5, c = 6
- Δ = 25 − 24 = 1
x = (5 ± 1)/2
- x = 3
- x = 2
Example 2: One Repeated Solution (Δ = 0)
Solve:
2x² + 4x + 2 = 0
- a = 2, b = 4, c = 2
- Δ = 16 − 16 = 0
x = −4 / 4 = −1
A zero discriminant signals a double root at x = −1
Example 3: Two Complex Solutions (Δ < 0)
Solve:
x² + 2x + 5 = 0
- a = 1, b = 2, c = 5
- Δ = 4 − 20 = −16
√(−16) = 4i
x = (−2 ± 4i)/2
x = −1 ± 2i
Quadratics always have two solutions in the complex number system, counting multiplicity.
Common Errors That Break Correct Work
@mrsmathsireland0 Solving a Quadratic Equation using -b formula… . . . #solvingaquadraticequation #quadraticformula #quadraticequations #mrsmathsireland #mathstok #juniorcert #leavingcert #gcsemaths #learnontiktok
Even small slips in signs, grouping, or arithmetic can derail an otherwise solid solution, which makes knowing the most common quadratic formula mistakes a practical advantage.
1. Losing the Sign of b
In x² − 7x + 10 = 0, b equals −7, not 7.
Write coefficients separately before substituting.
2. Dropping Parentheses
Correct structure:
x = ( −b ± √(b² − 4ac) ) / (2a)
Without parentheses, division happens in the wrong place.
3. Forgetting the Full Denominator
Everything above the fraction bar divides by 2a , not just the square root.
4. Rushing the Discriminant
b² and 4ac cause most arithmetic slips. Slow down there.
Where the Formula Comes From
Using the quadratic formula does not require knowing its origin, though the derivation helps with memory and confidence.
The formula comes from completing the square on:
ax² + bx + c = 0
Outline of the process:
- Divide both sides by a
- Move the constant term
- Add the square-completing term
- Factor the perfect square
- Take square roots
- Solve for x
After simplification, the quadratic formula appears exactly as written earlier.
Projectile Motion
Vertical motion under constant gravity produces quadratic equations. A typical height equation looks like:
y = y₀ + v₀ᵧt − (1/2)gt²
Setting y to ground level and solving for t produces two answers:
- One time while rising
- One time, while falling
Negative time often gets discarded when it represents a moment before launch. The ± symbol reflects real physical meaning, not abstract algebra.
Quadratic Formula on Standardized Tests
Standardized exams continue to expect comfort with the quadratic formula. Practice materials include problems where the formula appears explicitly in solution explanations.
Effective preparation focuses on:
- Fast recognition of a, b, c
- Accurate discriminant calculation
- Clean simplification of radicals and fractions
Practical Shortcuts That Save Time
A few small habits, applied before touching the quadratic formula, can cut down arithmetic, reduce errors, and make even messy equations move faster.
Reduce Before Solving
If every term shares a common factor, divide it out first.
Example:
6x² + 12x + 6 = 0
Divide by 6:
x² + 2x + 1 = 0
Simpler numbers reduce error risk.
Spot Perfect Squares
When Δ equals 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, roots turn out rational. Predicting solution type ahead of time helps plan simplification.
Handling Decimals and Fractions
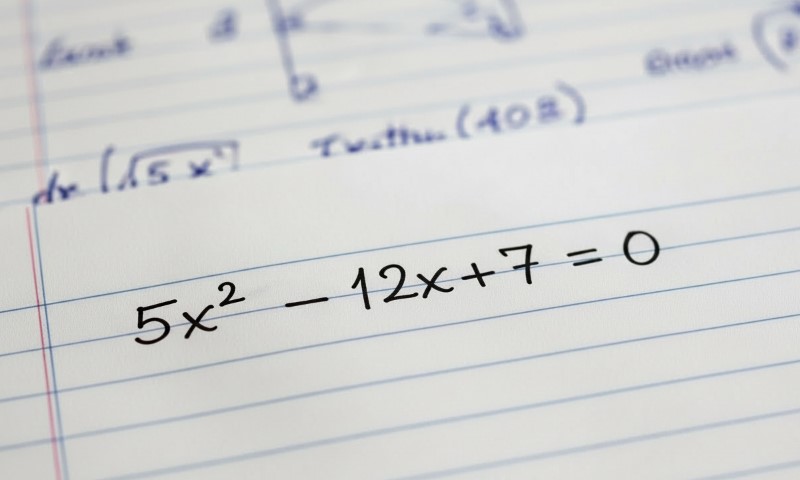
Decimals and fractions can make a quadratic look intimidating at first glance, but a few smart adjustments early on keep the quadratic formula clean, accurate, and manageable.
Decimals
Clear them early.
0.5x² − 1.2x + 0.7 = 0
Multiply by 10:
5x² − 12x + 7 = 0
Fractions
Stick with exact fractions until the end. Rounding early creates drift.
Numerical Stability in Computation
When solving quadratics inside programs or spreadsheets, subtraction between nearly equal numbers can cause loss of precision.
Numerical methods courses show alternative rearrangements that avoid cancellation and improve accuracy.
For hand calculations, the standard formula works well. For code, stability deserves attention.
A Final Checklist
- Rewrite in ax² + bx + c = 0
- Identify coefficients with signs
- Compute Δ = b² − 4ac
- Predict solution type
- Substitute carefully
- Split, simplify, and check
The quadratic formula earns its reputation by working every time. Use it patiently, keep the structure intact, and it delivers reliable results across algebra, science, and applied problems.
Related Posts: